




Notes:
For each LUT size in the X axis, we presented the same set of 600 color images to the system.
The first 75 images were used to compute the mean and standard deviation images used for background subtraction,
and the remaining 525 images showed a subject entering the volume, performing a series of motions, and exiting.
To perform these tests, the $RTS^3$ system was modified to work in batch mode.
The only sense in which batch mode differs from online mode is that the images are read off of the
hard disk instead of being read directly from the framegrabbers.
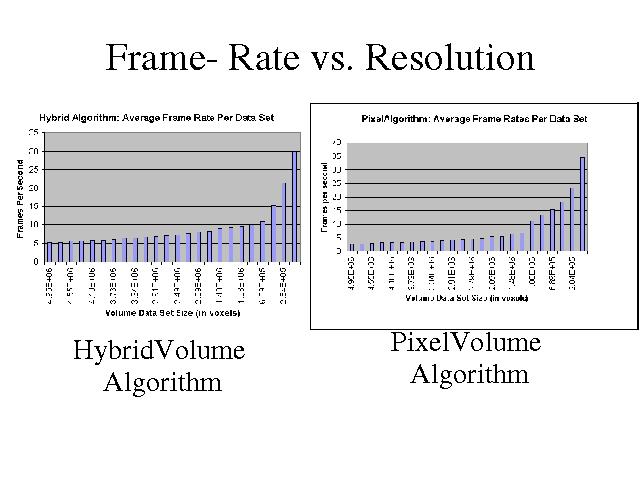
Using both approaches, the frame rate goes up dramatically as the number of voxels falls below 1 million.
Which we believe is due to cache locality.
The HybridVolume approach had frame rates that were twice as fast for the high resolution volumes.
However, this advantage does not show up at lower volumetric resolutions.
This suggests that the pixel-volume technique takes better advantage of cache locality than the hybrid volume algorithm










